


Atrial Fibrillation is a common cardiac arrhythmia where upper chambers of the heart are beating chaotically and fast and are out of sync with lower chambers. Based on the heart rate, some patients can feel symptoms of palpitations or shortness of breath due to this abnormal rhythm. If there are some other risk factors, this rhythm can pose the risk of a stroke and hence to be taken seriously.

Atrial Flutter
Atrial Flutter is a cardiac arrhythmia which is not that uncommon. Upper chambers of the heart are beating fast and regular with some synchronization to the lower chambers. Patients may feel symptoms of shortness of breath, palpitations or lightheaded. This rhythm can also pose some risk of stroke in patients with risk factors, if left untreated.

SVT
Supra ventricular tachycardia (SVT) is a broad term used for fast heart rates originating from either the junction where upper and lower heart chambers meet, or utilising this junction as a circuit in continuing fast heart rates (AVNRT). Some times, this arrhythmia is due to an extra nerve linking the upper and lower chambers present from birth (AVRT) and in some others it is due to a group of cells constantly firing impulses away from upper chamber (Atrial tachycardia).

Ventricular tachycardia
Ventricular tachycardia (VT) is an abnormal fast rhythm which originates from the lower chambers. Some VTs can result in light head/ dizziness, breathlessness and in some instances collapse/black out. Rarely these rhythms can be life threatening.
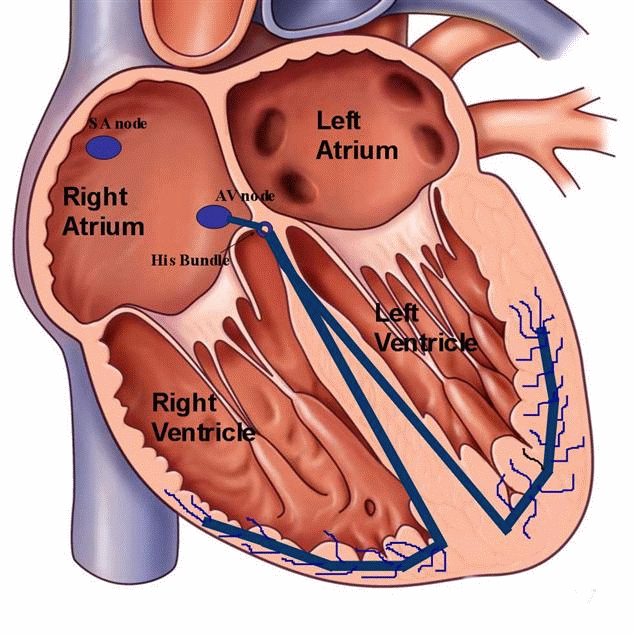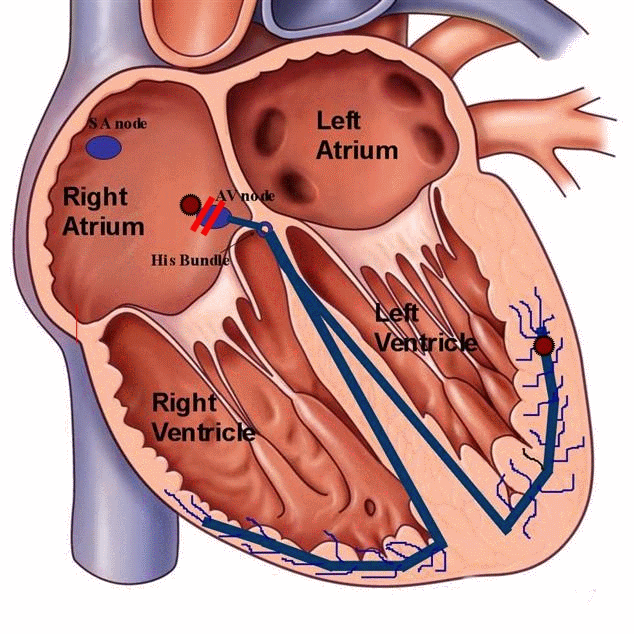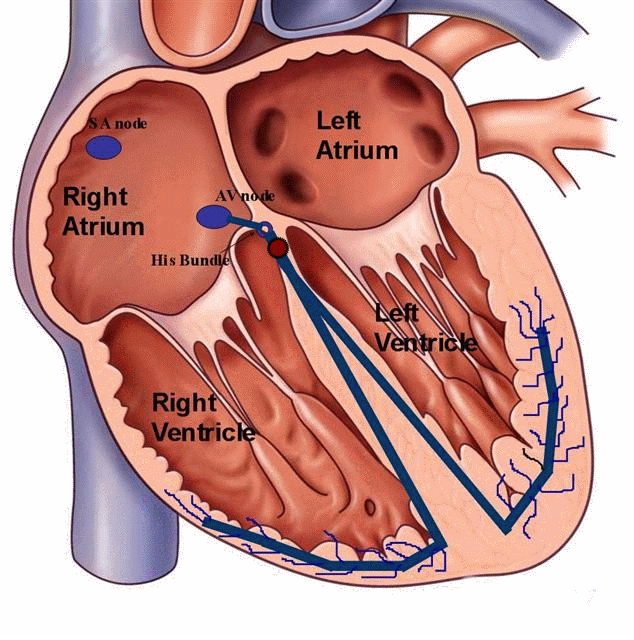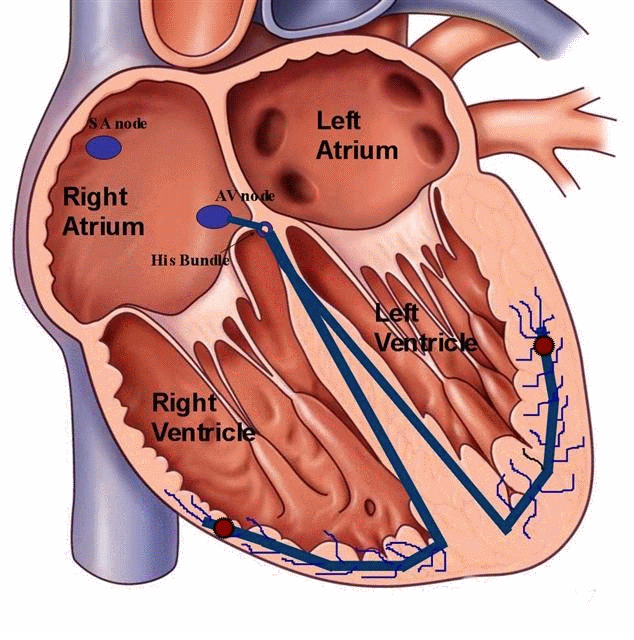
Bradycardia
Bradycardia refers to slow heart rate. Some times slow heart rate could be due to abnormality in communication (conduction) between upper and lower chambers ( heart blocks). This condition can result in dizziness, collapse, extreme fatigue and in some cases breathlessness. Some of these patients would benefit from pacemaker implantation.

Pacemakers and ICDs
Pacemakers are small battery operated devices which are inserted under the skin and underlying tissue below the collar bone. The procedure is done in a cathlab (operating theater) and takes about an hour. Pacemakers help when slow heart rhythms pose symptoms.
Implantable cardiac defibrillator (ICD) has all functions of a pacemaker, but in addition can also give shock in a life threatening arrhythmia conditions and potentially save a patient. This type of device is inserted if it is deemed that the patient is at high risk of developing life threatening arrhythmia.

CRT
In patients with poor pumping strength of the lower chambers of the heart ( Heart failure) sometimes a special pacemaker or defibrillator which has a third lead is inserted to the back wall of the left ventricle (lower chamber). This can help in better functioning of the heart pump and help with symptoms of patients.